
Faraday Rotator Mirror
Thermal and mechanical perturbations introduced to a standard, single-mode fiber often cause variations in the state of polarization (SOP) of the guided light. These changes can adversely effect the performance of many different types of systems. Retaining the SOP using polarization-maintaining (PM) fiber can reduce or eliminate these negative effects, but PM fiber is costly and often difficult to incorporate effectively.
The Faraday Rotator Mirror is a low-cost, passive device that correctly compensates for such SOP variations. This simple, easily installed component works to neutralize the effects caused by changes in the SOP, allowing engineers greater control over the design of systems such as fiber sensors, erbium-doped fiber amplifiers, tunable fiber lasers, etc.
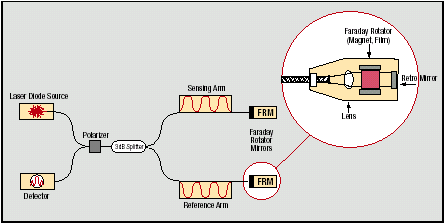
Principle
The Faraday Effect describes the non-reciprocal rotation of a signal's polarization as it passes through an optical medium within a magnetic field. Situated at the end of an optical fiber, the Faraday Rotator Mirror is designed to rotate a signal's SOP by 45°, twice-once when the light enters, and again when the light is reflected back into the fiber. Since the Faraday Effect is non-reciprocal, the resultant SOP is rotated by 90° with respect to the original signal.

A Faraday rotator is situated in front of the mirror. It is this element that provides the non-reciprocal 45° rotation of the state of polarization each time the light passes through it. These rotations, applied in combination with a reversal of the polarization state's handedness upon reflection at the mirror interface, yield a state that is perpendicular to the original signal.
In this way, any SOP fluctuations that occur anywhere along the fiber are exactly compensated and their unwanted effects neutralized.
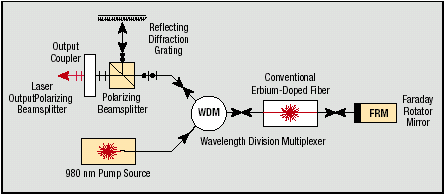
Design
Using a micro aspheric glass lens, light exiting the fiber is properly collimated through a Bismuth Iron Garnet (BIG) Faraday rotating element that is accurately positioned in the field of a permanent magnet. The beam, reflected at normal incidence by a dielectric coated mirror, retraces its original path and re-enters the fiber.
OFR's Faraday Rotator Mirrors are available off-the-shelf pigtailed with standard single mode fiber, Corning SMF 28 or equivalent. The fiber is mounted in a standard 900 mm tight tube buffer with proper strain relief.
Custom models are available upon special request.
Low-loss Models, unique to OFR, are selected for Insertion Loss less than 0.5 dB. Standard loss models are available at less than 0.8 dB. Also unique to OFR's FRMs is high power capability...2-3 W.
No other FRMs on the market can claim to match OFR's specifications.
Catalog
Number |
Model |
Wavelength |
Bandwidth |
Insertion
Loss |
Return
Loss |
Faraday
Rotation |
| MFI-1310-A |
Low loss |
1310 nm |
13 nm |
0.5 dB |
>55 dB |
45° ± 1° |
| MFI-1550-A |
Low loss |
1550 nm |
15 nm |
0.5 dB |
>55 dB |
45° ± 1° |
| MFI-1310-B |
Standard |
1310 nm |
13 nm |
0.8 dB |
>55 dB |
45° ± 1° |
| MFI-1550-B |
Standard |
1550 nm |
15 nm |
0.8 dB |
>55 dB |
45° ± 1° |
|

|

![]()